Macrolides
What are Macrolides?
Macrolides are a class of antibiotics derived from Saccharopolyspora erythraea(originally called Streptomyces erythreus), a type of soil-borne bacteria.
Macrolides inhibit protein synthesis in bacteria by reversibly binding to the P site of the 50S unit of the ribosome. Macrolides mainly affect gram-positive cocci and intracellular pathogens such as mycoplasma, chlamydia, and legionella. Erythromycin was the first macrolide discovered; other macrolides include azithromycin, clarithromycin, and roxithromycin.
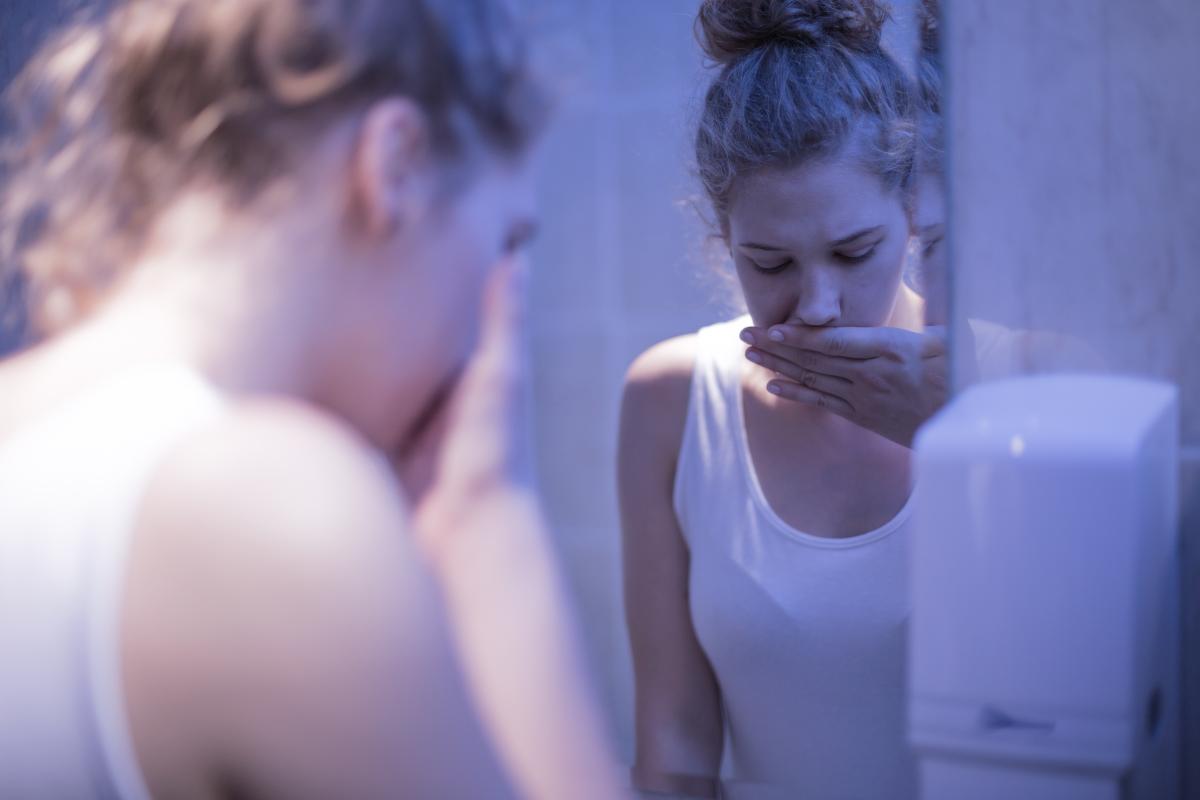
Their action is primarily bacteriostatic but may be bactericidal at high concentrations, or depending on the type of microorganism.
- Azithromycin.
- Clarithromycin.
- Difficid.
- E.E.S.
- Ery-Tab.
- EryPed.
- Erythrocin lactobionate.
- Erythrocin stearate.

The mechanism of action of macrolides is inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis, and they are thought to do this by preventing peptidyl transferase from adding the growing peptide attached to tRNA to the next amino acid (similarly to chloramphenicol) as well as inhibiting bacterial ribosomal translation.