Miscellaneous antihyperlipidemic agents
What are Miscellaneous antihyperlipidemic agents?
Miscellaneous antihyperlipidemic agents are used to treat hyperlipidemia. They help to decrease total cholesterol by lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides and raising high-density lipoproteins (HDL) cholesterol. Niacin (nicotinic acid) is a water-soluble B vitamin, which inhibits the synthesis of cholesterol and triglycerides, therefore lowers total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and raises HDL cholesterol levels.
Lipid-lowering agents, also sometimes referred to as hypolipidemic agents, cholesterol-lowering drugs, or antihyperlipidemic agents are a diverse group of pharmaceuticals that are used to lower the level of lipids and lipoproteins, such as cholesterol, in the blood (hyperlipidemia).
Antihyperlipidemics include different classes of medications, among which some of the most commonly used are HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, also called statins. Statins include simvastatin, rosuvastatin, atorvastatin, lovastatin, and pravastatin, which are administered orally.
Types of cholesterol-lowering drugs include: Statins (Lipitor®, Crestor®, Zocor® and others). PCSK9 inhibitors (Praluent®, Repatha® and Leqvio®).

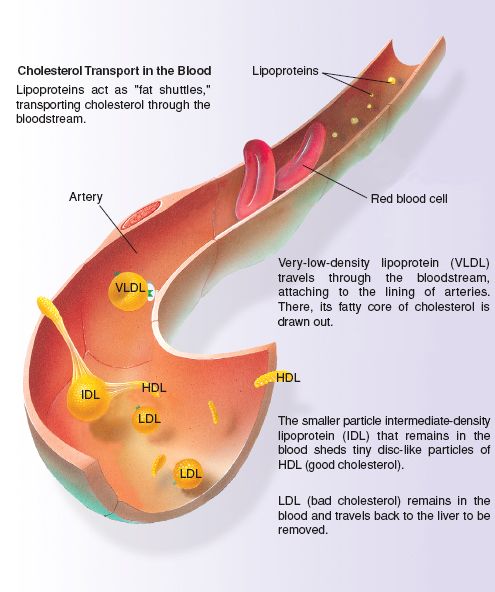
Miscellaneous (Derived) lipids are the derivatives of simple and compound lipids and have the common properties of lipids. Steroids, hydrocarbons, carotenoid, and fat- soluble vitamins are examples of this group.
The widely used antihyperlipidemic drug is statins. Patients can take niacin, fibrates, and bile acid sequestrants based on the lipid levels in the body. These antihyperlipidemic drugs have unique mechanisms of actions; some can take weeks to work on the body while other medications may cause side effects.
Fibrates are medicines prescribed to help lower high triglyceride levels. Triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood. Fibrates also may help raise your HDL (good) cholesterol. High triglycerides along with low HDL cholesterol increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Classification. Hyperlipidemias may basically be classified as either familial (also called primary) when caused by specific genetic abnormalities or acquired (also called secondary) when resulting from another underlying disorder that leads to alterations in plasma lipid and lipoprotein metabolism.
Statins also classify as lipophilic or hydrophilic. Lipophilic statins include simvastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin. Hydrophilic statins include pravastatin, fluvastatin, and rosuvastatin.
Hypercholesterolemia can be primary, secondary to another disease or condition, or multifactorial. The primary forms, in turn, can be genetic or idiopathic (Table 1). All genetic hypercholesterolemia is primary, but not all primary presentations of hypercholesterolemia are genetic.
An antilipemic agent is a type of drug that is included in the category of agents acting on metabolic diseases and endocrine functions. It is specifically used to lower lipid levels in the blood, such as cholesterol and triglycerides.
Statins. This class of drugs, also known as HMG CoA reductase inhibitors, works in the liver to prevent cholesterol from forming. This reduces the amount of cholesterol circulating in the blood. Statins are most effective at lowering LDL (bad) cholesterol.