Miscellaneous bone resorption inhibitors
What are Miscellaneous bone resorption inhibitors?
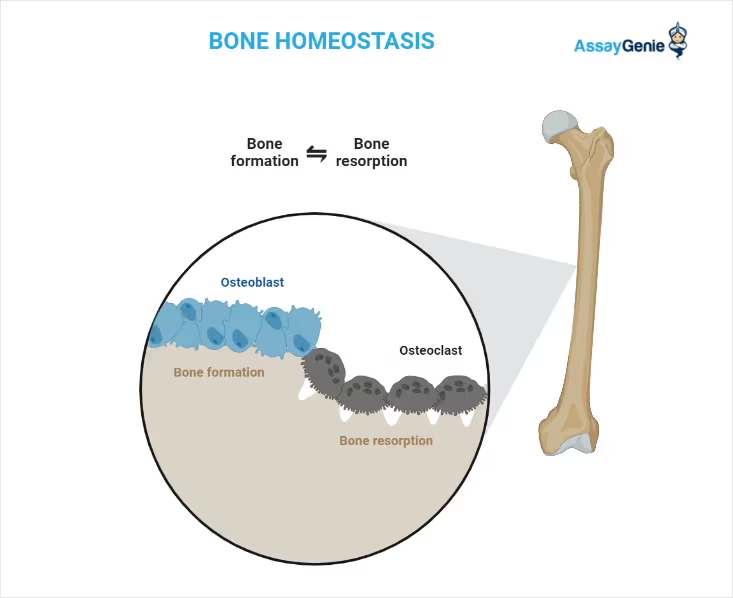
Miscellaneous bone resorption inhibitors are drugs that inhibit mineralization or resorption of the bone. These agents work by different mechanisms to decrease bone resorption and prevent calcium loss from the bones. These bone resorption inhibitors are used to treat patients who have bone cancer or to treat patients who have excess calcium in the blood due to cancer.
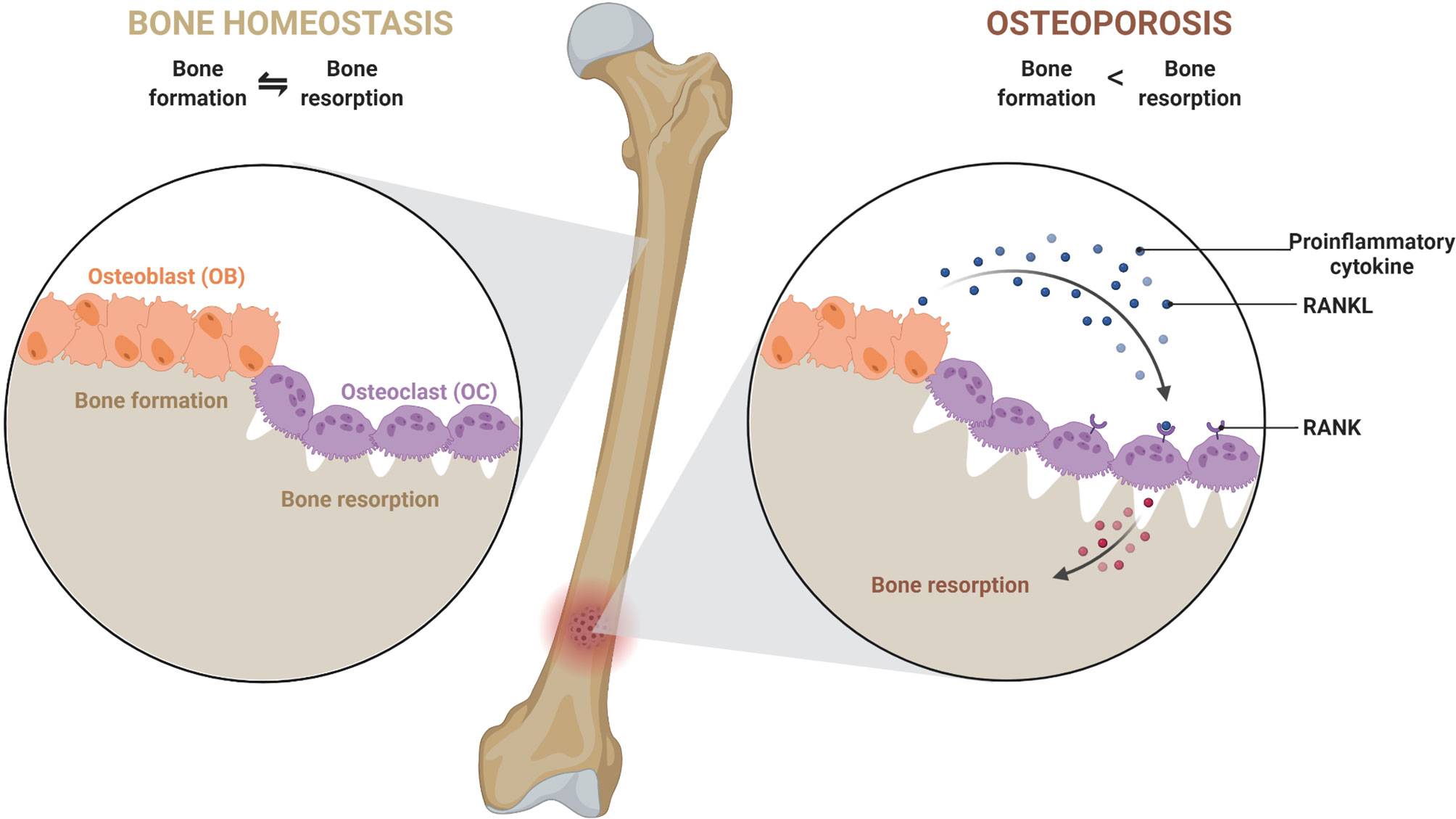
What are Bone resorption inhibitors? Bone resorption inhibitors are drugs that inhibit mineralization or resorption of the bone by blocking the action of osteoclasts. They are used to treat postmenopausal and glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, Paget’s disease of the bone and malignant hypercalcemia.
Estrogen Inhibits Bone Resorption by Directly Inducing Apoptosis of the Bone-resorbing Osteoclasts.
There are mainly three kinds of anti-osteoporosis drugs: (1) Anti-bone resorption drugs include bisphosphates (such as alendronate, zoledronic acid, risedronate, ibandronate, etidronate and clodronate, etc.), calcitonin (such as elcatonin and salcatonin), selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs)

We have recently shown that a carboxyl-terminal sequence of parathyroid hormone-related protein, PTHrP[107-139], is a potent direct inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption.
Bone resorption inhibitors are primarily used to treat and prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Other uses include treatment of osteoporosis due to other causes, including corticosteroid therapy, treatment of Paget’s disease of the bone, and management of hypercalcemia.
List of Miscellaneous bone resorption inhibitors
Prolia