Antituberculosis agents
What are Antituberculosis agents?
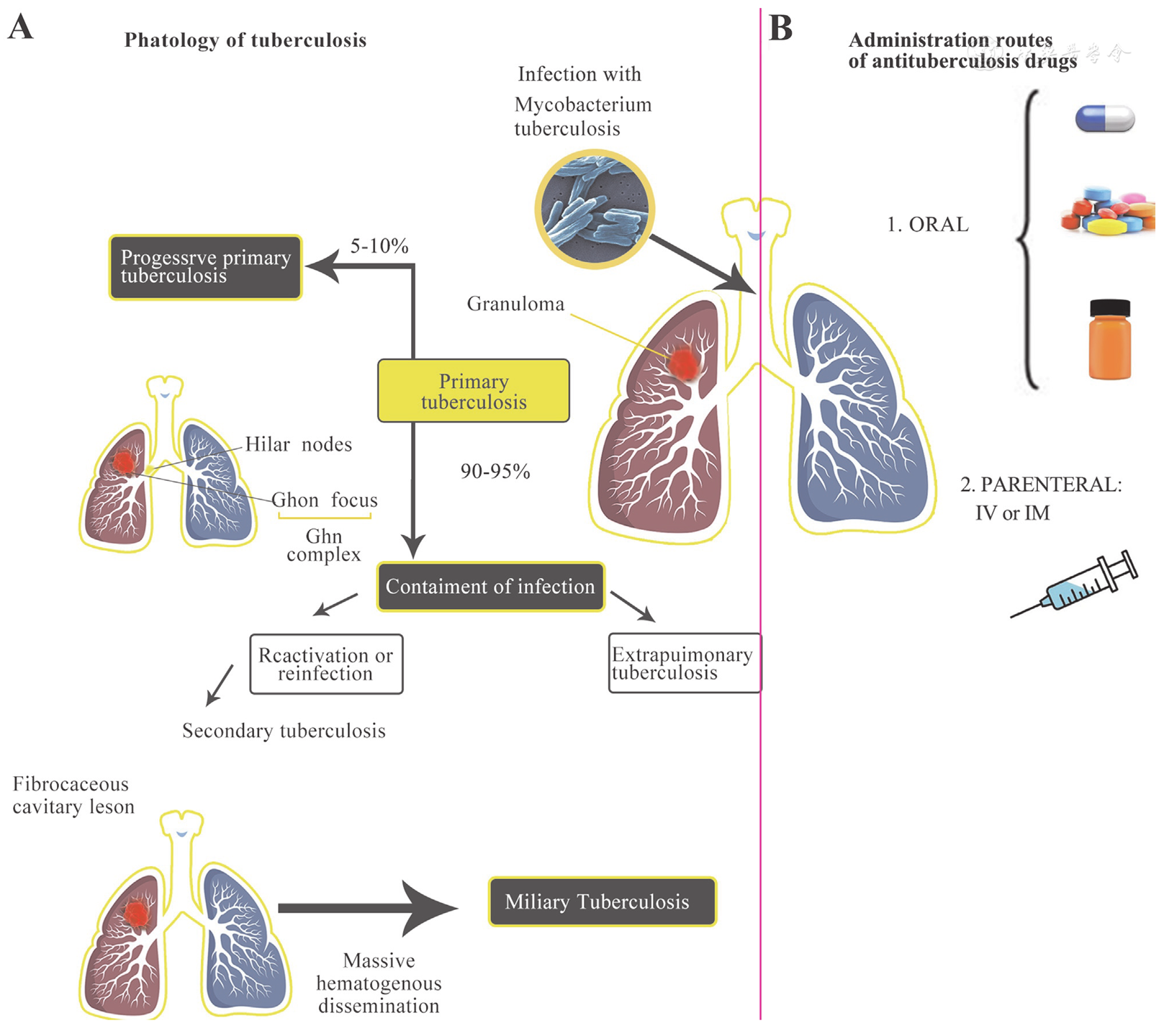
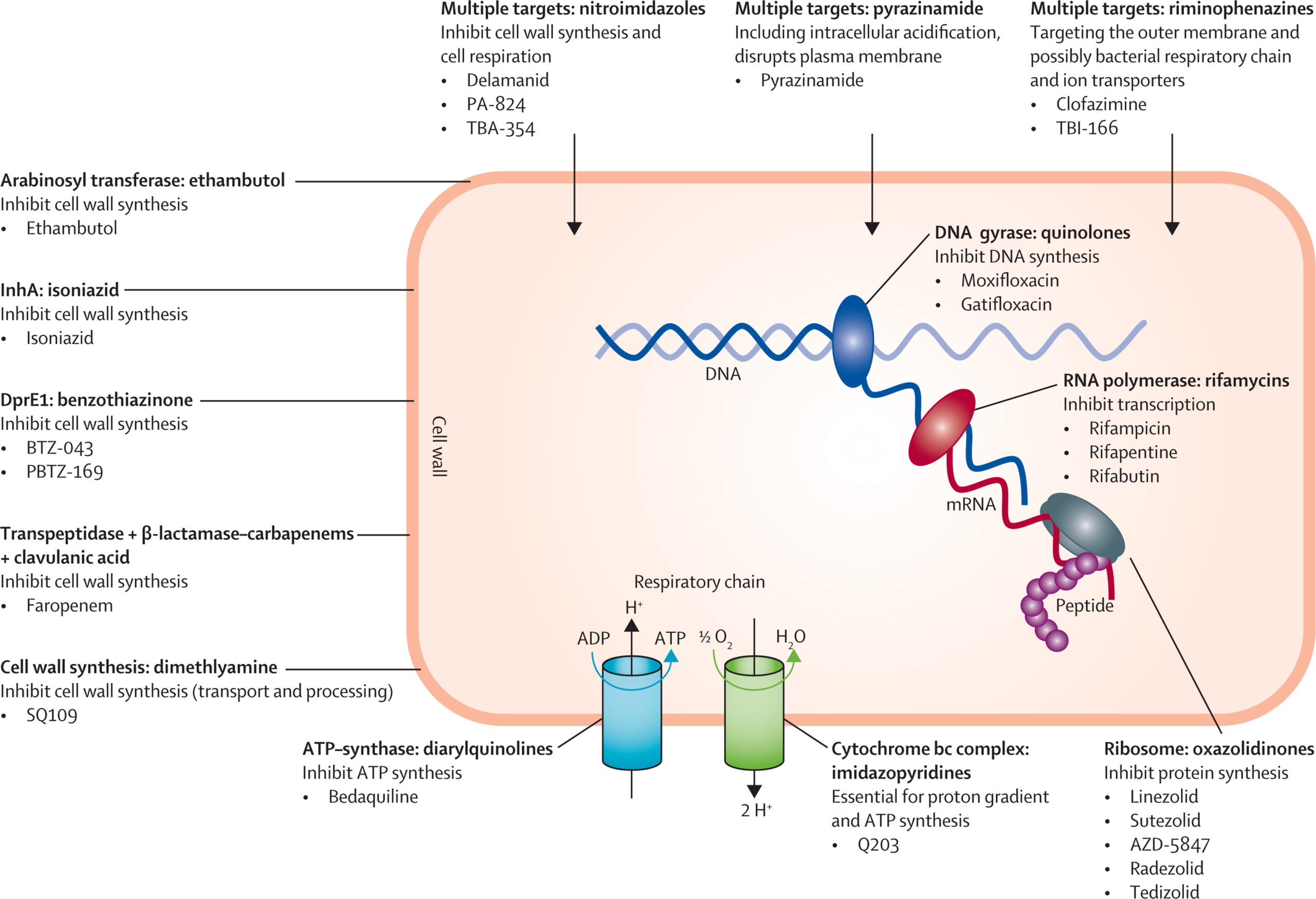
Antituberculosis agents are drugs used to treat tuberculosis, an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This infection mainly affects the lungs but can also affect many other organ systems. Many classes of drugs, with different mechanism of action have activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis chemotherapy involves giving two to four drugs simultaneously. These drugs work differently so they target the organism in different ways and using a few types of drugs prevents drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium from evolving.

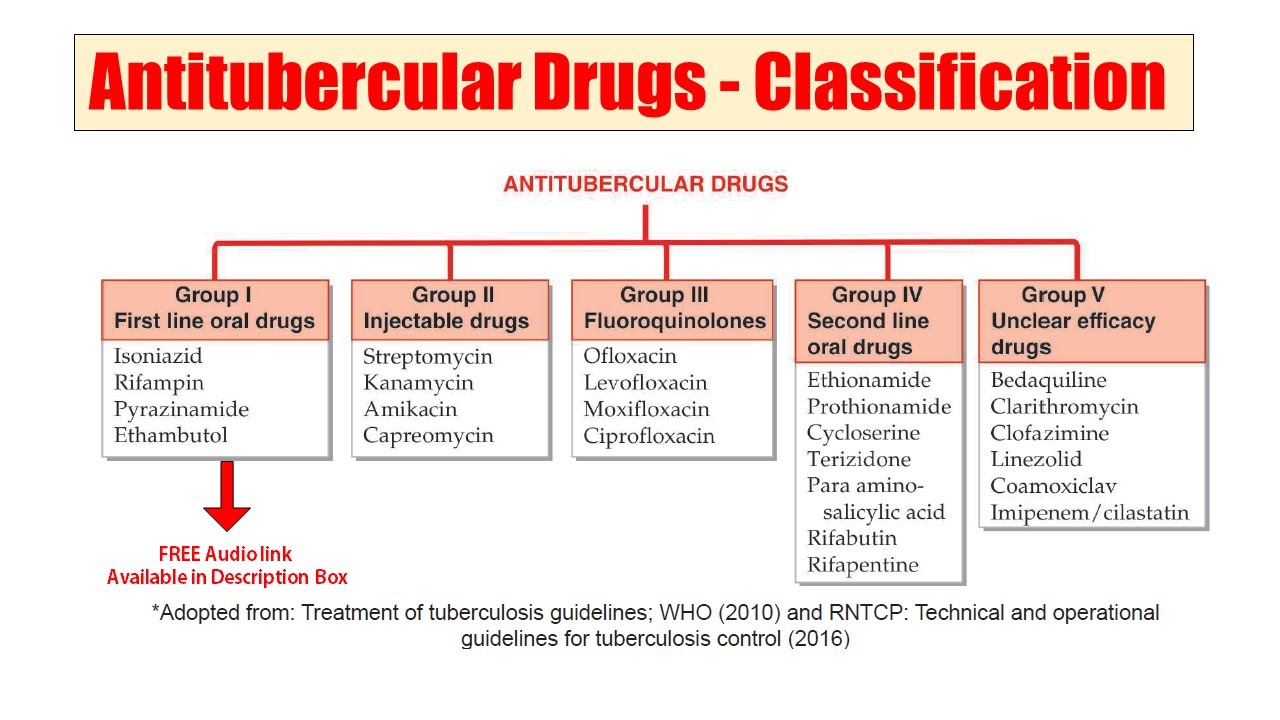
Antitubercular medications: rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol are FDA approved to treat Mycobacterium tuberculosis infections. Antitubercular medications are a group of drugs used to treat tuberculosis.
The current standard WHO‐approved regimen consists of isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol (HRZE) for two months (intensive phase), followed by isoniazid and rifampicin with ethambutol (HRE) in areas of high resistance, or without ethambutol (HR) for four months (continuation phase) (WHO 2010).
List of Antituberculosis agents
Balsalazide
Canasa
Giazo
Isoniazid
Lialda
Mesalamine
Pentasa
Rifampin
Rowasa