SGLT-2 inhibitors
Other names: SGLT2 inhibitors, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors
What are SGLT-2 inhibitors?
SGLT-2 inhibitor is an abbreviation for sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors. SGLT-2 inhibitors are a class of medicine used to lower high blood glucose levels in people with type 2 diabetes. They may also be called gliflozins.
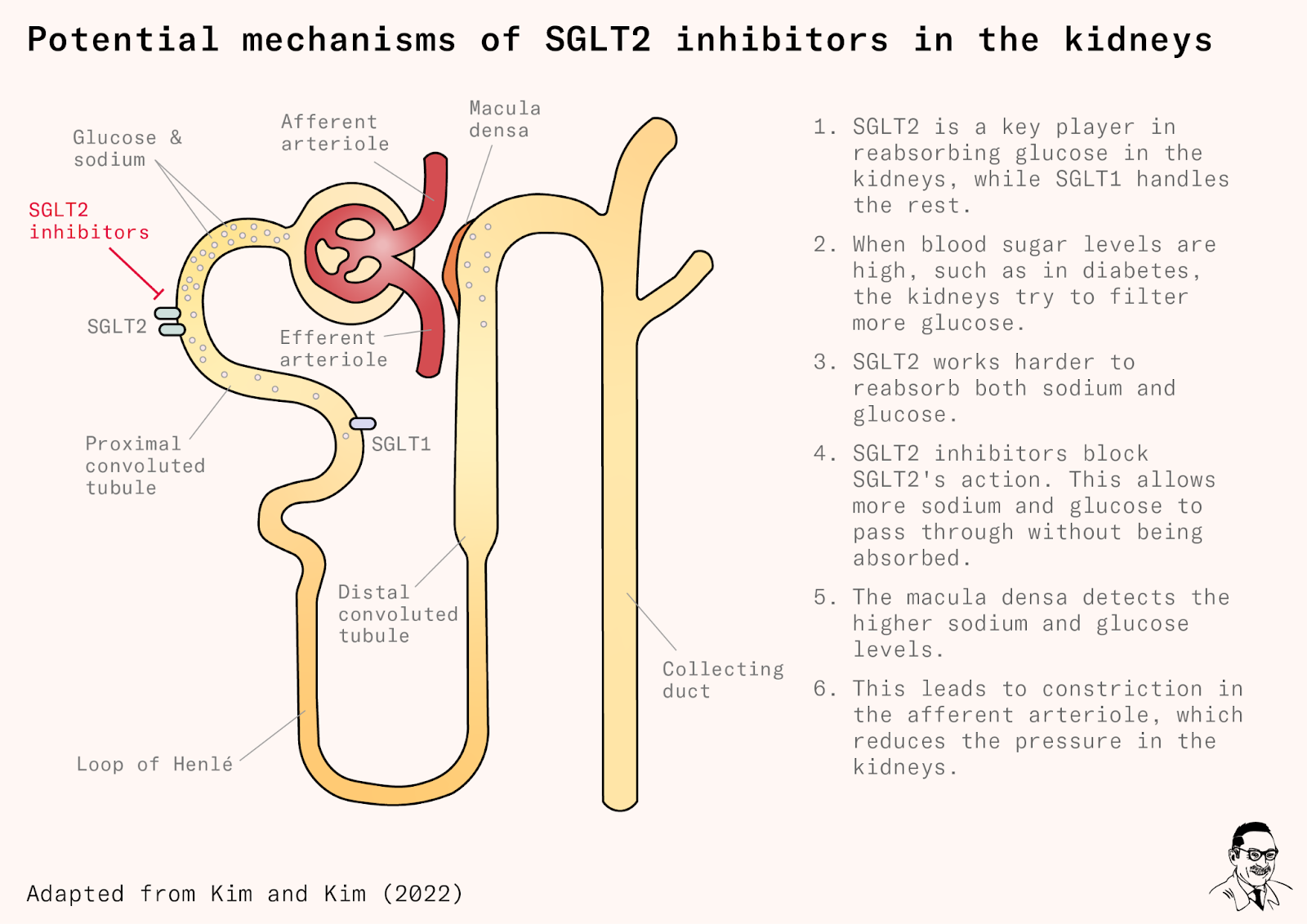
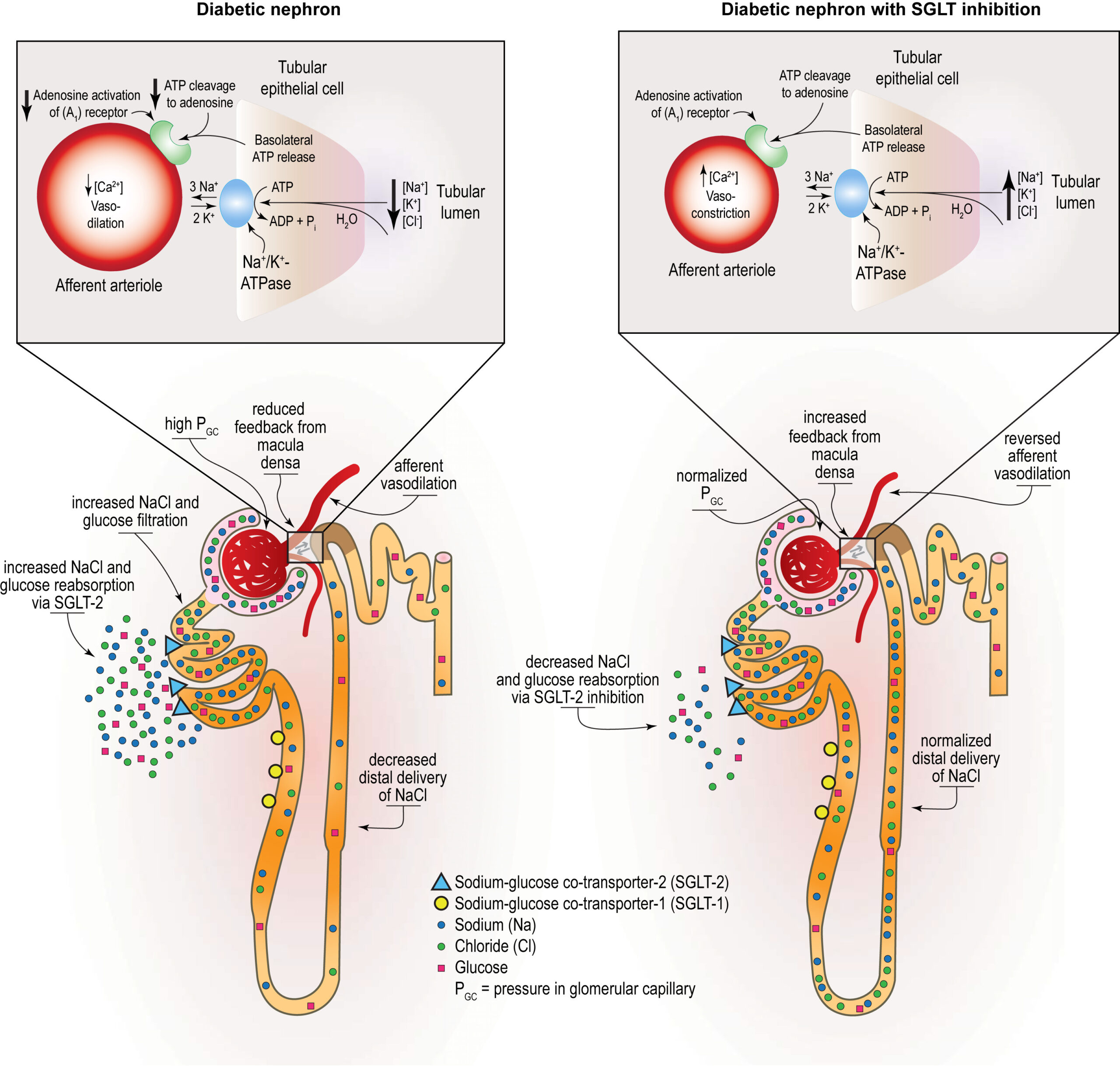
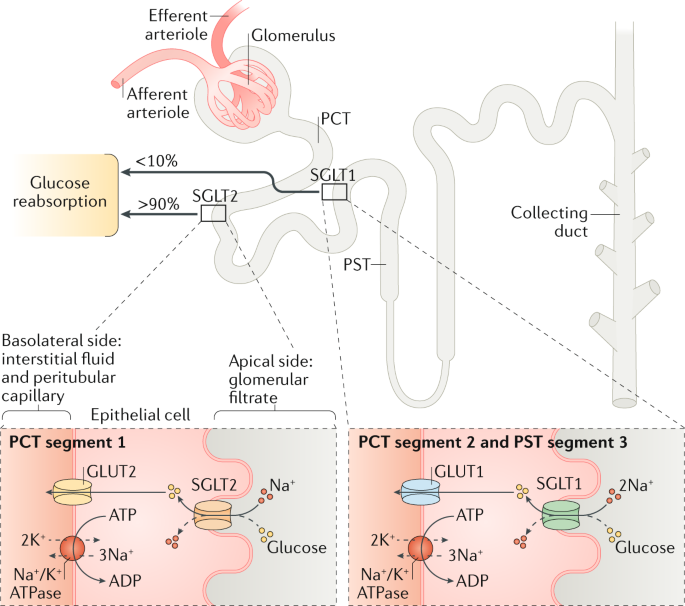
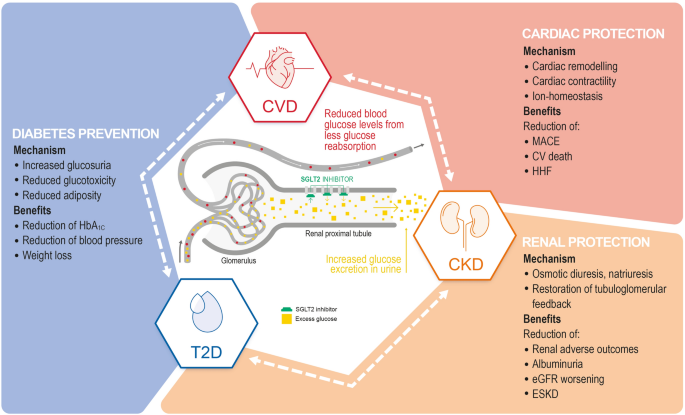
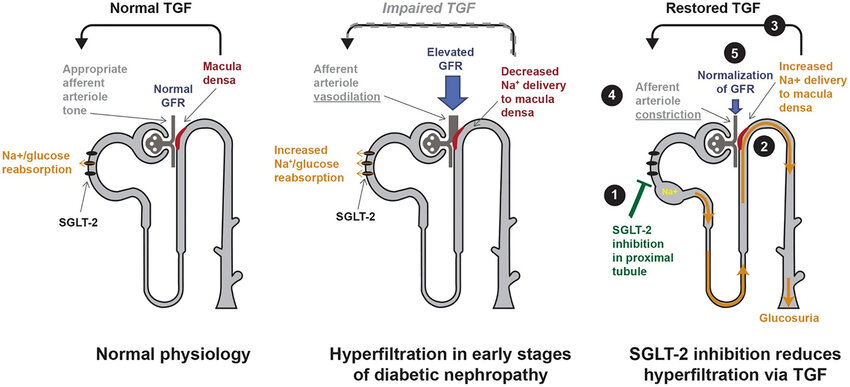
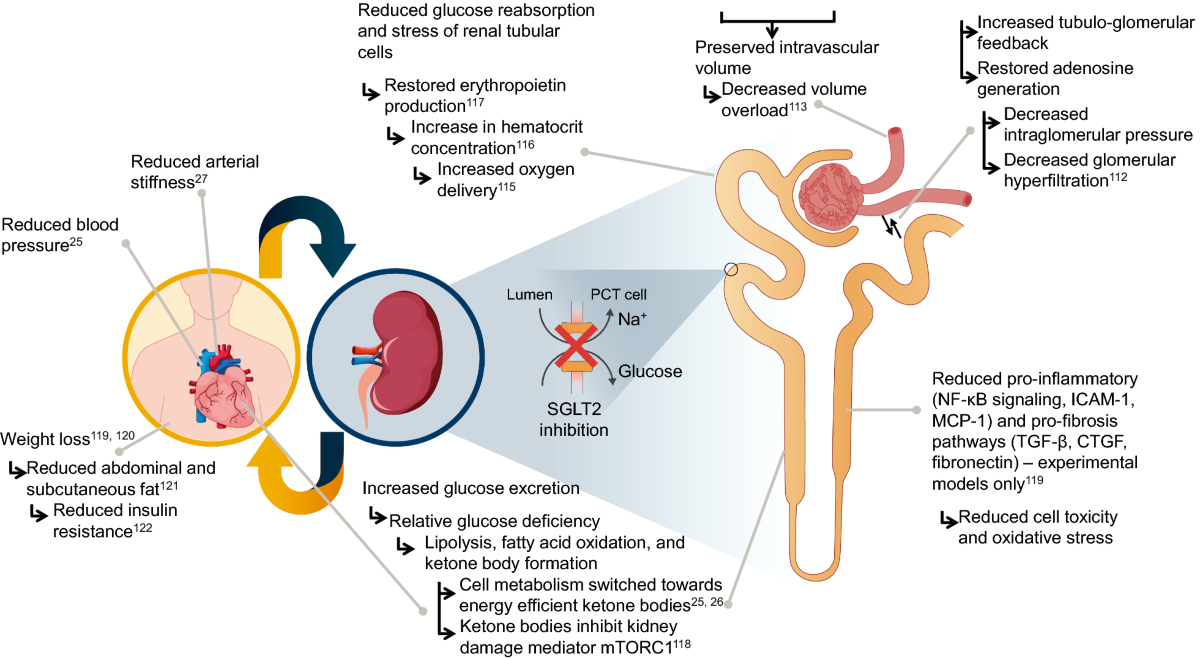
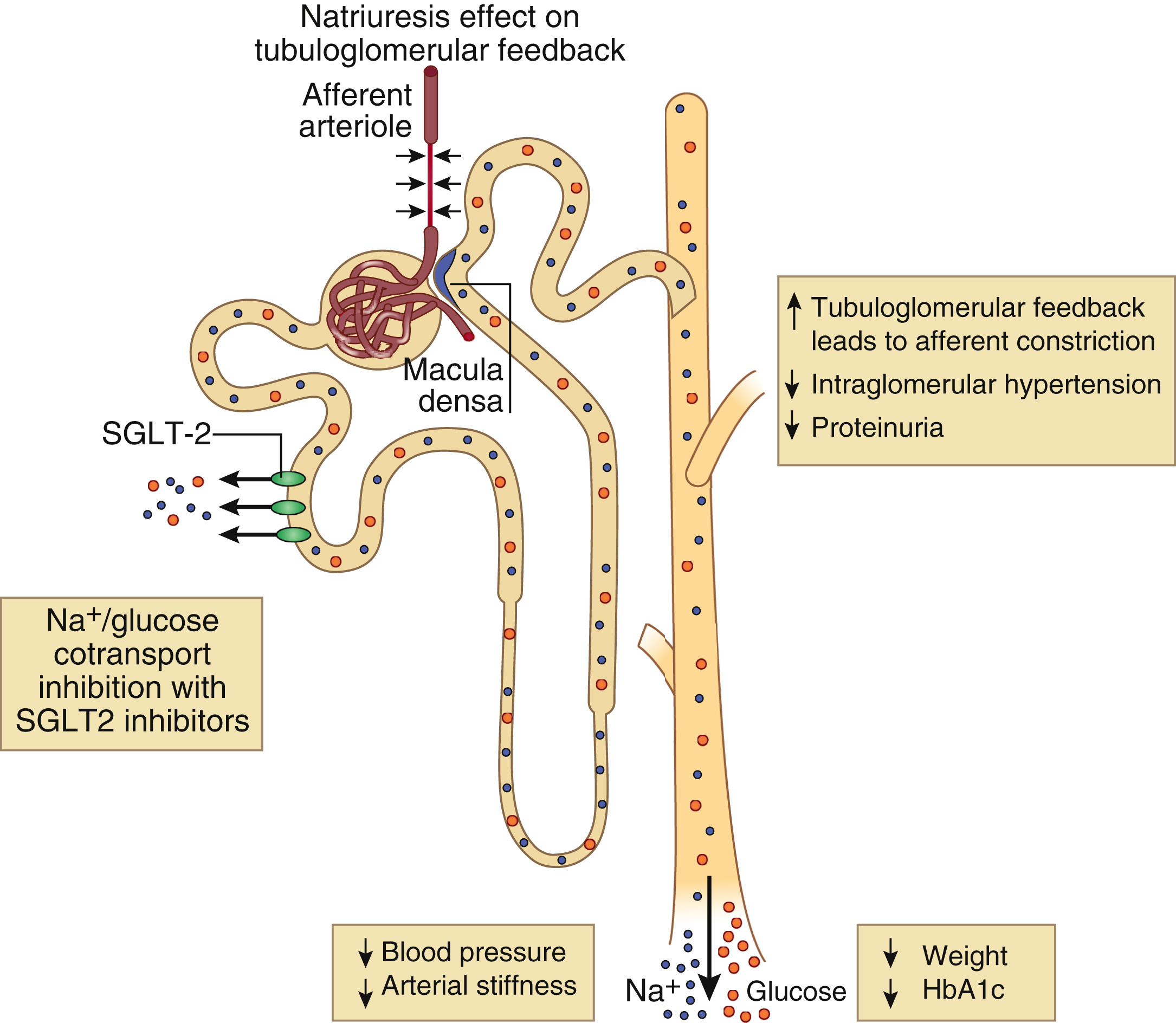
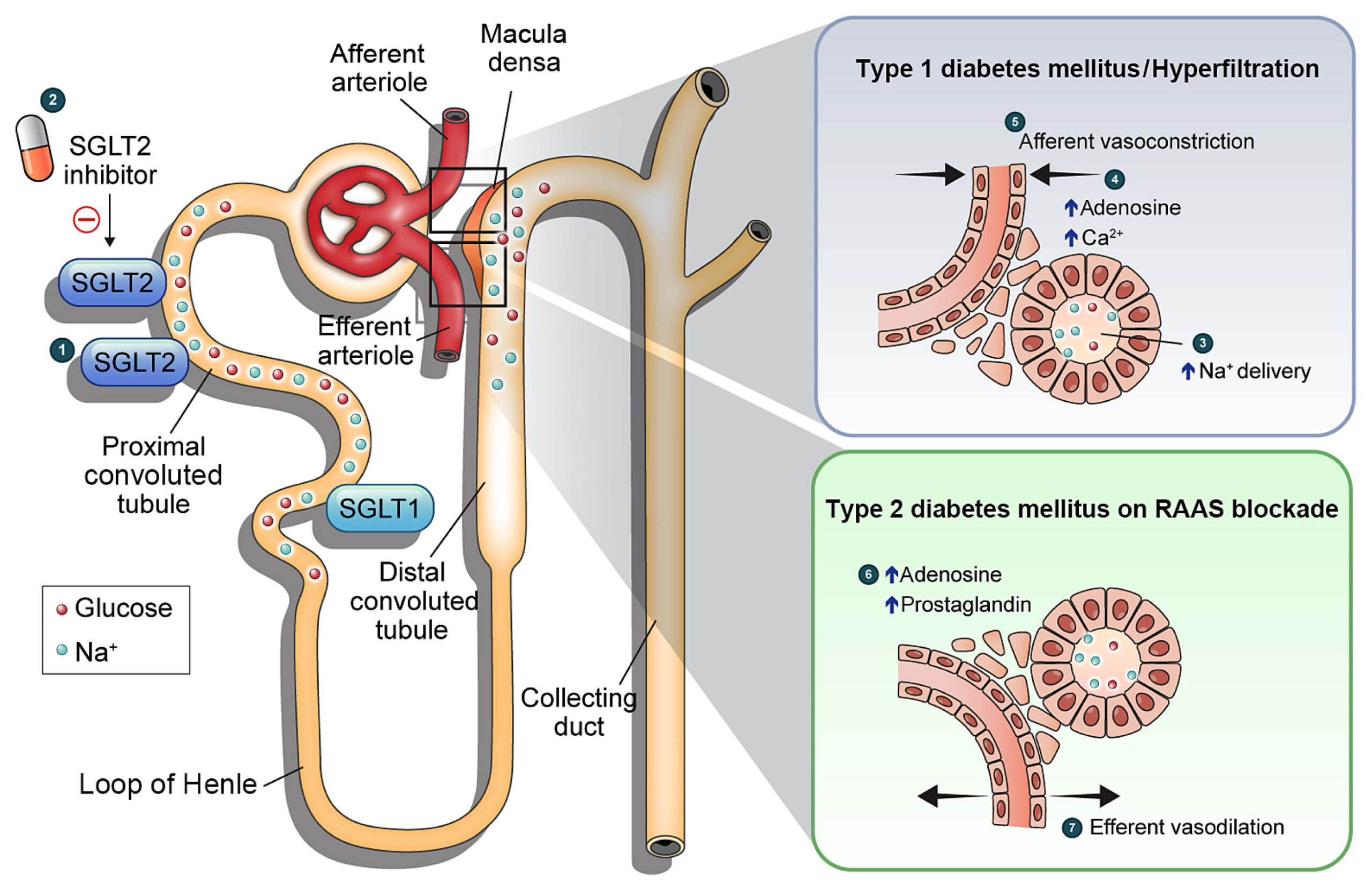
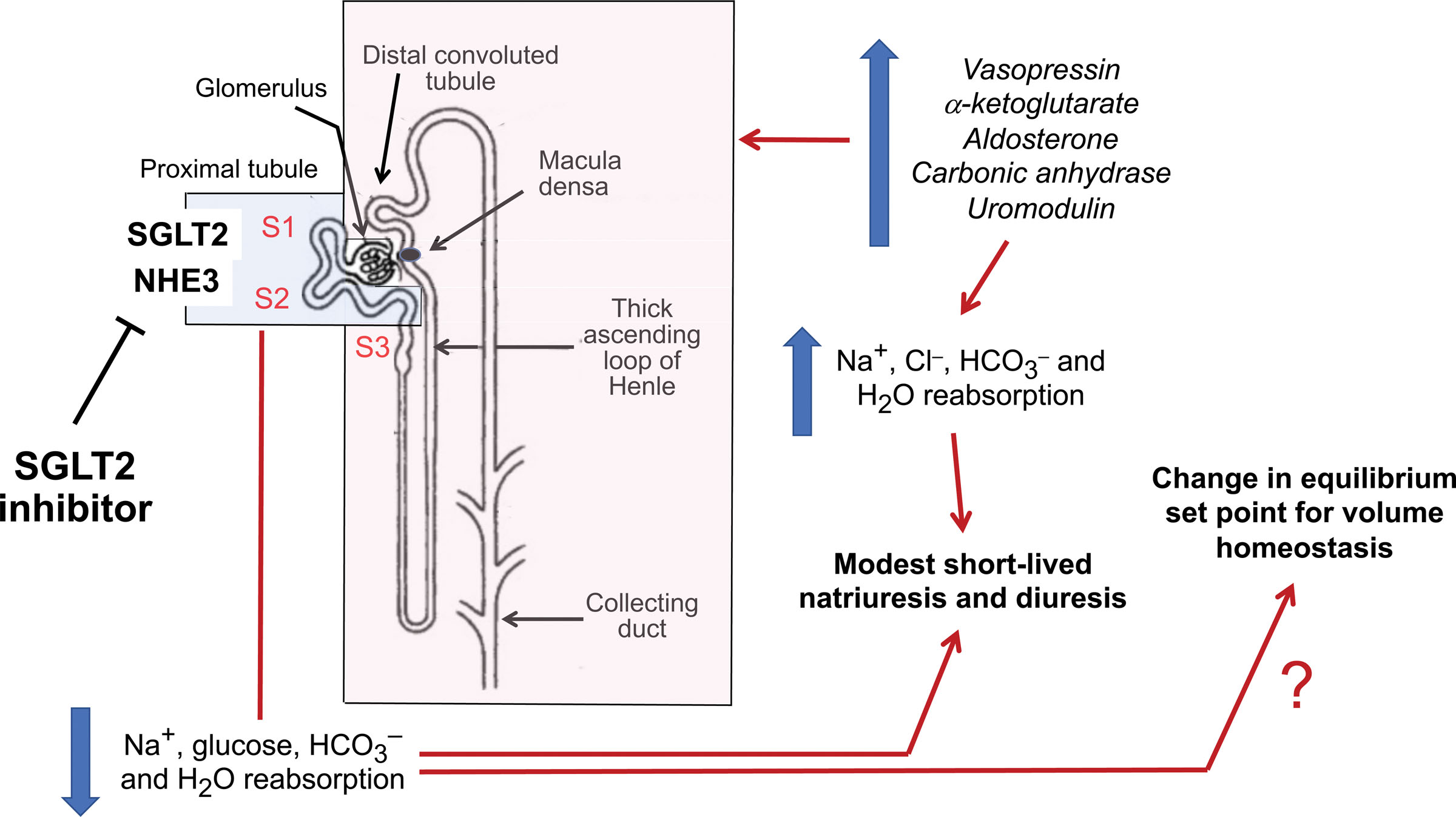
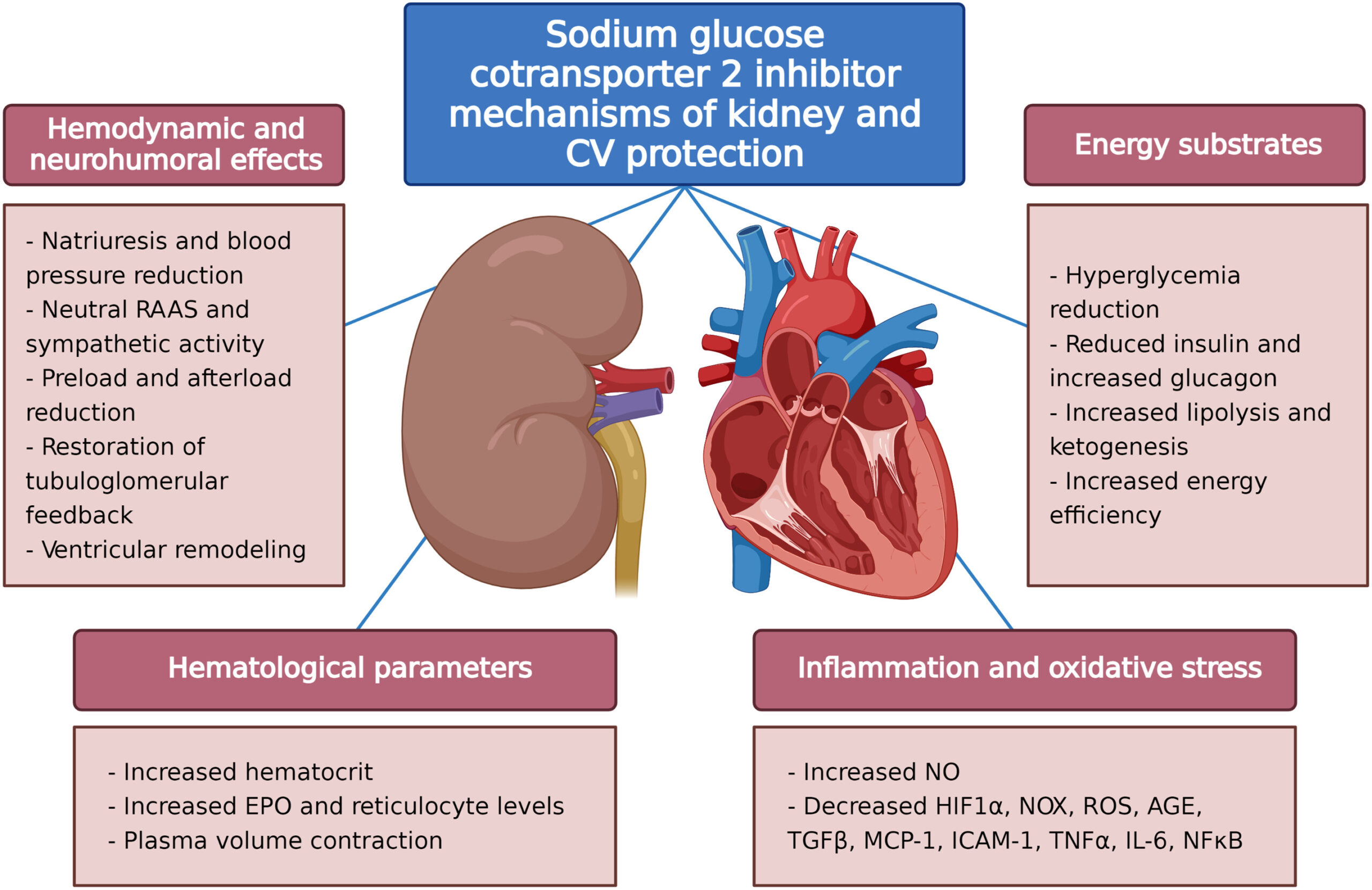
SGLT-2 inhibitors inhibit SGLT-2 proteins located in the renal tubules of the kidneys which are responsible for reabsorbing glucose back into the blood. As a result, more glucose is excreted in the urine. SGLT-2 inhibitors have been shown to be effective at lowering hemoglobin A1c levels, improving weight loss and lowering blood pressure. They carry a low risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar levels).
They are usually well tolerated. SGLT-2 inhibitors may be used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes and act independently of beta-cell function in the pancreas.
What are SGLT2 inhibitors? Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors, often called SGLT2 inhibitors, are used to manage blood sugar levels. They can be taken on their own or with other diabetes medications such as metformin, sulphonylureas or insulin.
SGLT-2 inhibitors have a novel mechanism of action that is independent of insulin secretion and action. These agents block glucose reabsorption, leading to urinary glucose excretion. The advantages of this approach are reduced hyperglycemia without hypoglycemia, along with weight loss and blood pressure reduction.

- bexagliflozin (Brenzavvy)
- canagliflozin (Invokana)
- dapagliflozin (Farxiga)
- empagliflozin (Jardiance)
- ertugliflozin (Steglatro)
List of SGLT-2 inhibitors
Jardiance