Multikinase inhibitors
What are Multikinase inhibitors?
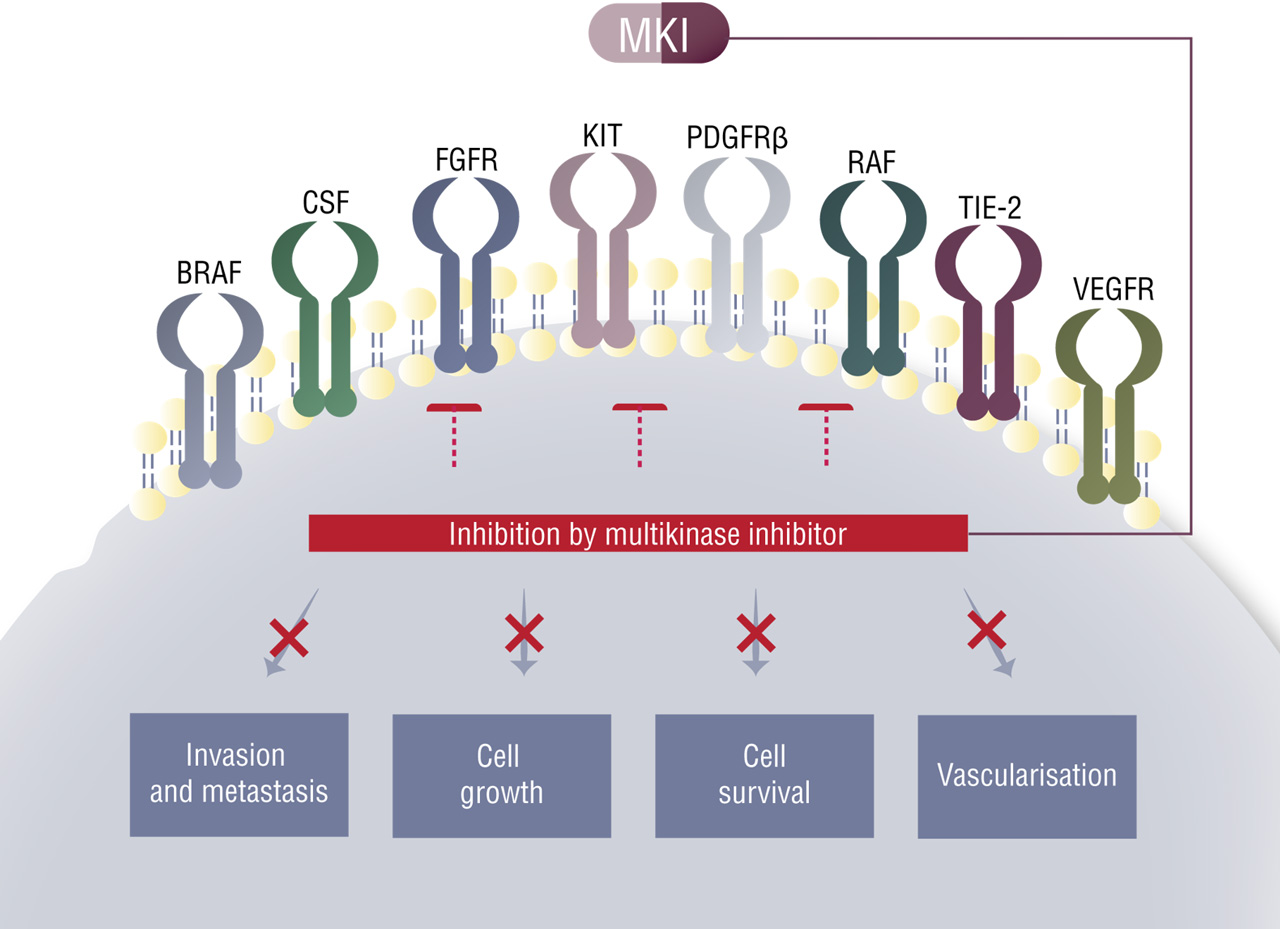
Multikinase inhibitors work by inhibiting multiple intracellular and cell surface kinases, some of which are implicated in tumor growth and metastatic progression of cancer, thus decreasing tumor growth and replication. Multikinase inhibitors may be used to treat advanced kidney cancer as well as other specific types of cancer.
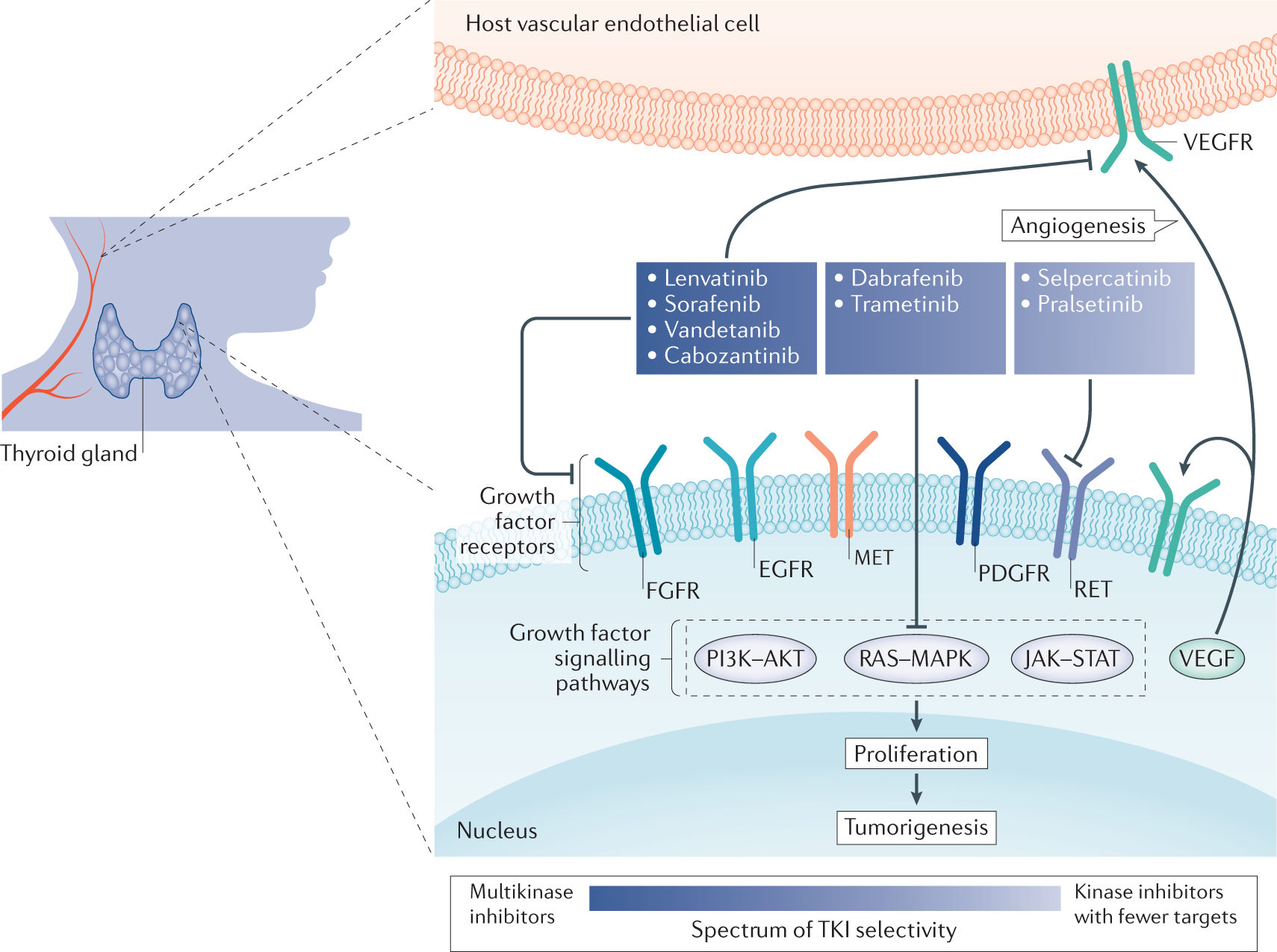
During recent years, a new treatment option with multikinase inhibitors (MKIs) such as sunitinib, sorafenib, lenvatinib, pazopanib, vandetanib, and cabozantinib has shown promising results in otherwise treatment-refractory thyroid cancer
Enzyme inhibitors can be used as drugs to inhibit chemical processes. These include Acyclovir (fighting herpes), methotrexate (fighting bacterial infections as well as cancers), Trazadone (combating depression), and ciglitazone (to address inflammatory diseases).
To date, many Type I kinase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer have been approved by the FDA viz. bosutinib, crizotinib, dasatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, lapatinib, pazopanib, ruxolitinib, sunitinib, and vemurafenib
Approved fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitors include erdafitinib, pemigatinib, and futibatinib. We review the most common toxicities associated with FGFR inhibitors and provide practical advice regarding their management.

Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors
| Drug | Target | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Erdafitinib | alpha1-acid glycoprotein | carrier |
| Futibatinib | Cytochrome P450 3A4 | enzyme |
| Futibatinib | ATP-dependent translocase ABCB1 | transporter |
| Futibatinib | Broad substrate specificity ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2 | transporter |
List of Multikinase inhibitors
Alunbrig
Sama Mohamed
August 26, 2025
Cabometyx
Sama Mohamed
February 13, 2026
Gavreto
Sama Mohamed
November 10, 2025
Gomekli
Sama Mohamed
October 25, 2025
Iclusig
Sama Mohamed
October 3, 2025
Inlyta
Sama Mohamed
October 2, 2025
Inrebic
Sama Mohamed
October 2, 2025
Jakafi
Sama Mohamed
September 27, 2025
Koselugo
Sama Mohamed
September 20, 2025
Lorlatinib
Sama Mohamed
September 12, 2025
Ofev
Sama Mohamed
September 1, 2025
Ojjaara
Sama Mohamed
September 1, 2025
Qinlock
Sama Mohamed
August 28, 2025
Quizartinib
Sama Mohamed
August 28, 2025
Retevmo
Sama Mohamed
August 28, 2025
Rydapt
Sama Mohamed
August 27, 2025