Non-iodinated contrast media
What are Non-iodinated contrast media?
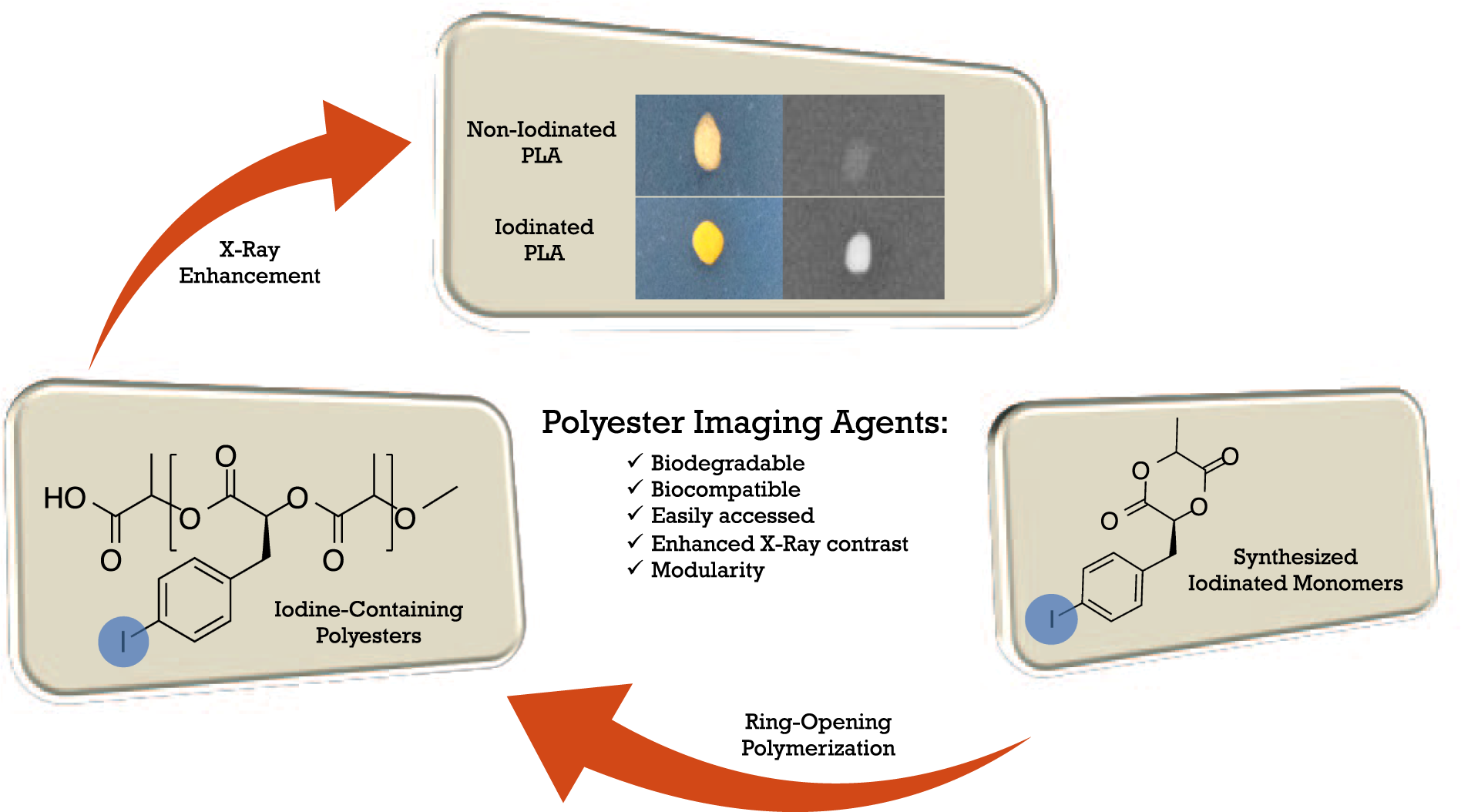
Contrast media is used in radiography to increase the clarity of the image. A non-iodinated contrast media is one that does not contain iodine and may instead contain barium or other non-iodinated media as the radio opaque substance.
Unlike contrast agents used in X-rays or CT scans, MRI contrast agents do not contain iodine and rarely cause allergic reactions or other problems. Hundreds of millions of doses of GBCA have been given to patients throughout the world since these agents were first developed and approved for use in 1988.
iso-osmolar non-ionic dimers (e.g. iodixonal, iotrolan). They are mainly used intravascularly, but can also be injected into body cavities particularly the low-osmolar contrast agents. They are also suitable for oral or rectal administration.
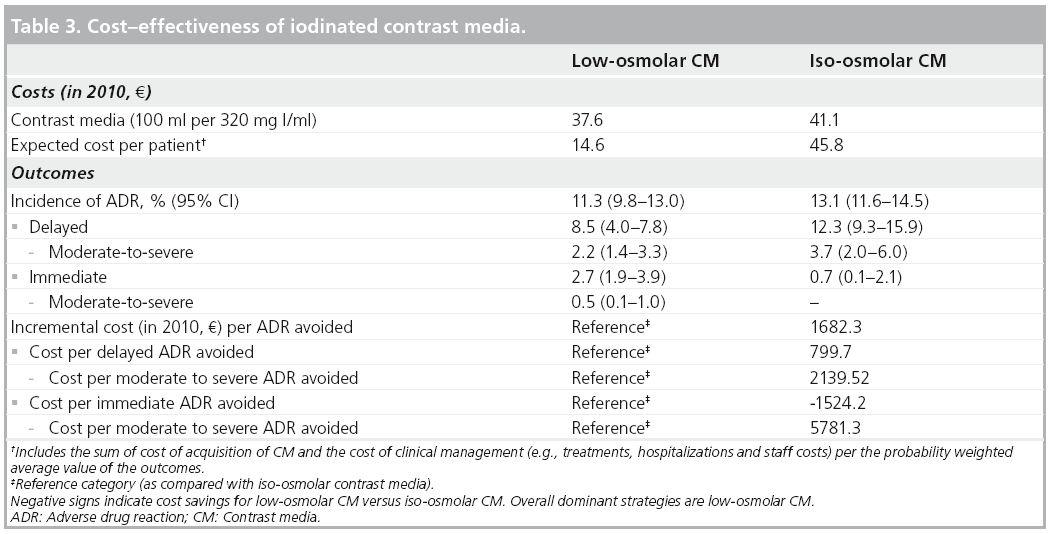
Diatrizoate meglumine (GastroView) and diatrizoate sodium (Hypaque) are examples of iodinated contrast used for fluoroscopic examinations, typically at a 20% concentration. These agents can also be used in a more dilute form for CT examinations (usually 2% to 3% concentration).
Many scans are routinely done without contrast, when visibility would be sufficient for a diagnosis. Non-contrast CT scans are also useful in situations where the use of contrast agents may be contraindicated, such as in patients with kidney problems or allergies to contrast.

Nonionic contrast medium refers to a type of contrast agent that is water-soluble and has largely replaced ionic contrast media due to its lower risk of adverse reactions, making it the preferred choice for patients with allergies, renal failure, and other serious conditions.
List of Non-iodinated contrast media
Olopatadine (nasal)
Oxymetazoline nasal
QNASL